Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is often associated with children, but it’s a condition that can persist into adulthood. Understanding Adult ADHD is crucial for those who live with it and for those who support them. This article aims to shed light on the symptoms, causes, impacts, and management strategies for Adult ADHD.
What is ADHD?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness. These symptoms can significantly interfere with daily functioning and quality of life.
Symptoms of Adult ADHD
ADHD in adults manifests differently than in children. Here are the primary symptoms categorized into inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity:
Inattention:
- Difficulty sustaining attention on tasks or activities
- Poor organizational skills
- Frequent careless mistakes in work or other activities
- Avoidance of tasks requiring prolonged mental effort
Hyperactivity:
- Restlessness, often feeling “on the go”
- Difficulty sitting still during meetings or in other quiet settings
- Excessive talking
Impulsivity:
- Interrupting others frequently
- Impatience in queues or waiting turns
- Making hasty decisions without considering long-term consequences
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of ADHD are not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute:
Genetics: ADHD tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
Brain Structure: Studies have shown differences in the brain anatomy of people with ADHD, particularly in areas that control attention and impulse control.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins during pregnancy, premature birth, and low birth weight are some environmental risk factors.
Impact of ADHD on Daily Life
ADHD affects various aspects of an adult’s life, from professional endeavors to personal relationships.
Work and Career:
- Job instability due to difficulties in time management and organization
- Procrastination and missed deadlines
- Struggles with maintaining consistent performance
Relationships:
- Miscommunication with partners, friends, and family
- Impulsivity leading to unplanned actions or statements
- Difficulty maintaining long-term relationships due to inconsistent behavior
Mental Health:
- Increased risk of anxiety and depression
- Low self-esteem stemming from ongoing challenges and setbacks
- Feelings of frustration and inadequacy
Diagnosis of Adult ADHD
Diagnosing ADHD in adults involves a comprehensive assessment by healthcare professionals.
Assessment:
- Clinical evaluation by a psychiatrist or psychologist
- ADHD rating scales and questionnaires to measure symptom severity
- Detailed personal history, including childhood behavior
Treatment Options
Managing ADHD often requires a multifaceted approach, combining medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Medication:
- Stimulants (e.g., Adderall, Ritalin) are commonly prescribed to enhance focus and reduce impulsivity.
- Non-stimulants (e.g., Strattera) are alternatives for those who do not respond well to stimulants.
Therapy:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps in modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Coaching and skills training provide practical strategies for managing daily tasks.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular exercise to improve overall well-being and reduce symptoms.
- Healthy diet and proper nutrition to support brain function.
- Good sleep hygiene to ensure adequate rest and reduce symptom exacerbation.
Coping Strategies
In addition to treatment, adopting effective coping strategies can significantly improve daily functioning.
Organizational Tools:
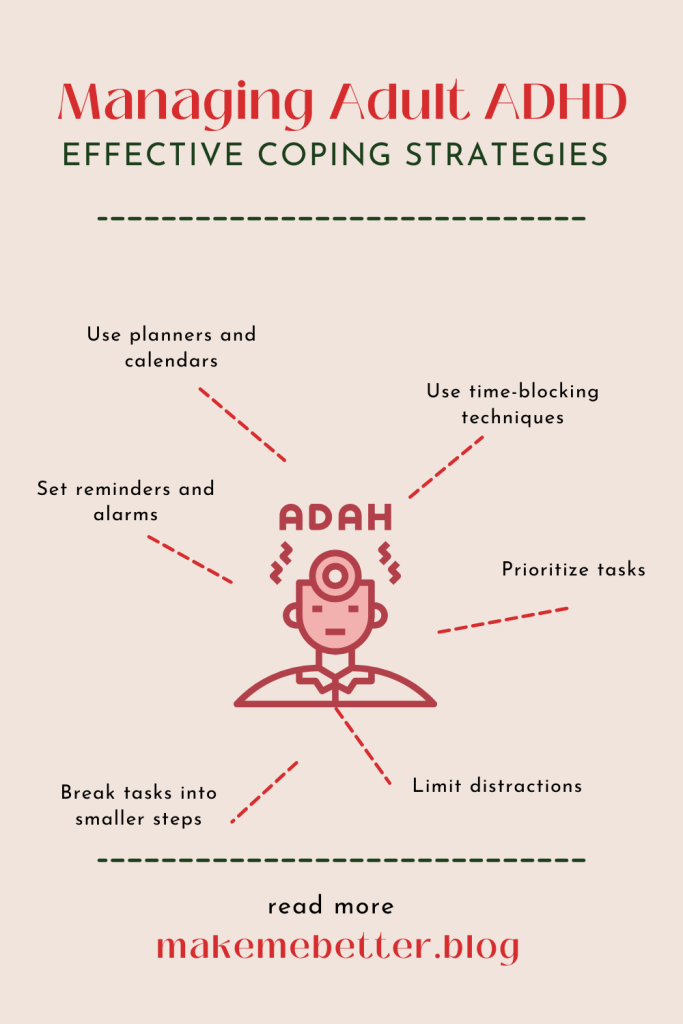
- Use planners and calendars to keep track of tasks and deadlines.
- Set reminders and alarms for important activities.
- Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
Time Management:
- Prioritize tasks by importance and urgency.
- Use time-blocking techniques to allocate specific periods for focused work.
- Minimize distractions by creating a quiet, dedicated workspace.
Self-Care:
- Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques to manage stress.
- Seek support from friends, family, or support groups.
- Join ADHD support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges.
Myths vs. Facts
Myth: ADHD is just a lack of willpower.
- Fact: ADHD is a medical condition with neurobiological roots.
Myth: Only children have ADHD.
- Fact: ADHD often persists into adulthood, affecting many aspects of life.
Myth: People with ADHD can’t focus on anything.
- Fact: People with ADHD may hyperfocus on tasks they find interesting, sometimes to the detriment of other responsibilities.
Resources
For those seeking more information or support, here are some recommended resources:
Books:
- “Driven to Distraction” by Dr. Edward M. Hallowell and Dr. John J. Ratey
- “You Mean I’m Not Lazy, Stupid or Crazy?!” by Kate Kelly and Peggy Ramundo
Websites:
Understanding Adult ADHD is the first step toward managing it effectively. By recognizing symptoms, seeking proper diagnosis, and employing appropriate treatment and coping strategies, individuals with ADHD can lead fulfilling and successful lives. If you or someone you know might have ADHD, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
Leave a comment