
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is crucial for maintaining healthy bones, supporting immune function, and reducing inflammation. Despite its importance, many people worldwide suffer from vitamin D deficiency. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and ways to overcome vitamin D deficiency to ensure optimal health.
What is Vitamin D and Why is it Important?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in calcium absorption, bone health, and immune function. It exists in two main forms: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). While our bodies can produce vitamin D3 when exposed to sunlight, D2 is primarily obtained from plant-based foods and supplements.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
Several factors can contribute to vitamin D deficiency, including:
- Limited Sun Exposure: Spending too much time indoors, living in higher latitudes, or covering your skin with clothing or sunscreen can reduce your exposure to UVB rays, which are necessary for vitamin D synthesis.
- Skin Pigmentation: Melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, can reduce the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. People with darker skin tones are at higher risk of deficiency.
- Age: As we age, our skin’s ability to produce vitamin D decreases, and our kidneys become less efficient at converting it to its active form.
- Diet: A diet low in vitamin D-rich foods can contribute to deficiency, especially for those following vegan or vegetarian diets.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and chronic kidney disease, can impair vitamin D absorption and metabolism.
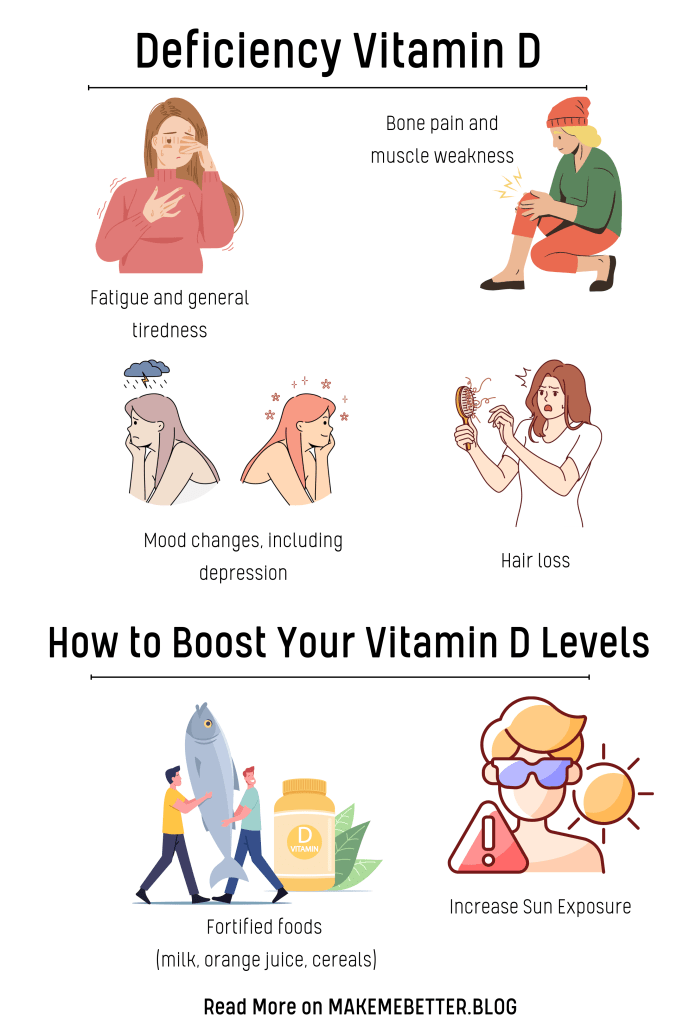
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency can manifest in various ways, including:
- Fatigue and general tiredness
- Bone pain and muscle weakness
- Mood changes, including depression
- Impaired wound healing
- Hair loss
In severe cases, prolonged deficiency can lead to rickets in children and osteomalacia or osteoporosis in adults, conditions characterized by weak or brittle bones.
How to Boost Your Vitamin D Levels
Addressing vitamin D deficiency involves a combination of sun exposure, dietary changes, and supplementation. Here are some effective strategies:
- Increase Sun Exposure: Aim to spend 10-30 minutes in the sun several times a week, exposing your arms, legs, and face. The exact time needed varies based on skin tone, geographic location, and time of year. Always be mindful of the risk of skin cancer and avoid prolonged exposure without protection.
- Consume Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Incorporate foods high in vitamin D into your diet, such as:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Cod liver oil
- Fortified foods (milk, orange juice, cereals)
- Egg yolks
- Cheese
- Mushrooms exposed to UV light
- Take Supplements: Vitamin D supplements are available in both D2 and D3 forms. D3 is generally considered more effective at raising blood levels of vitamin D. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage based on your specific needs.
- Use UV Lamps: In regions with limited sunlight, especially during the winter months, UV lamps or bulbs designed to produce UVB radiation can be a helpful alternative for stimulating vitamin D production.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is essential for overall health and well-being. By understanding the causes and symptoms of deficiency and implementing strategies to boost your vitamin D intake, you can protect yourself from the adverse effects of deficiency and support your body’s vital functions. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
For more health tips and wellness advice, be sure to explore the rest of our blog.
Leave a comment